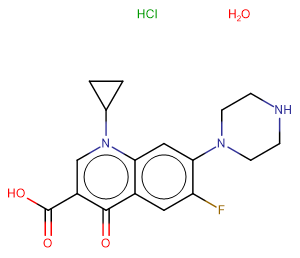
Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate
CAS No. 86393-32-0
Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate( Bay-09867 hydrochloride monohydrate | Ciloxan | Ceprimax | Oftacilox )
Catalog No. M21202 CAS No. 86393-32-0
Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate is a fluoroquinolone antibioticis an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCiprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCiprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate is a fluoroquinolone antibioticis an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections.
-
DescriptionCiprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate is a fluoroquinolone antibioticis an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections.(In Vitro):Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (5-50 μg/mL; 0-24 h; tendon cells) inhibits cell proliferation and causes cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate shows potent activity against Y. pestis and B. anthracis with MIC90 of 0.03 μg/mL and 0.12 μg/mL, respectively.(In Vivo):Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (30 mg/kg; i.p.; for 24 hours; BALB/c mice) has protection against Y. pestis in murine model of pneumonic plague.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloridemonohydrate (100 mg/kg; i.g.; daily, for 4 weeks; C57BL/6J mice) accelerates aortic root enlargement and increases the incidence of aortic dissection and rupture by decreases LOX level and increases MMP levels and activity in the aortic wall.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (100 mg/kg; i.g.; daily, for 4 weeks; C57BL/6J mice) induces DNA damage and release of DNA to the cytosol, mitochondrial dysfunction, and activation of cytosolic DNA sensor signaling. Ciprofloxacin lactate increases apoptosis and necroptosis in the aortic wall.
-
In VitroCiprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (5-50 μg/mL; 0-24 h; tendon cells) inhibits cell proliferation and causes cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate shows potent activity against Y. pestis and B. anthracis with MIC90 of 0.03 μg/mL and 0.12 μg/mL, respectively.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:Tendon cells Concentration:5, 10, 20 and 50 μg/mL Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Decreased the cellularity of tendon cells.Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:Tendon cellsConcentration:50 μg/mL Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Arrested cell cycle at the G2/M phase and inhibited cell division in tendon cells.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:Tendon cells Concentration:50 μg/mL Incubation Time:0, 6, 12, 17 and 24 hours Result:Down-regulated the expression of CDK-1 and cyclin B protein and mRNA. Up-regulatedthe expression of PLK-1 protein.
-
In VivoCiprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (30 mg/kg; i.p.; for 24 hours; BALB/c mice) has protection against Y. pestis in murine model of pneumonic plague.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (100 mg/kg; i.g.; daily, for 4 weeks; C57BL/6J mice) accelerates aortic root enlargement and increases the incidence of aortic dissection and rupture by decreases LOX level and increases MMP levels and activity in the aortic wall.Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) hydrochloride monohydrate (100 mg/kg; i.g.; daily, for 4 weeks; C57BL/6J mice) induces DNA damage and release of DNA to the cytosol, mitochondrial dysfunction, and activation of cytosolic DNA sensor signaling. Ciprofloxacin lactate increases apoptosis and necroptosis in the aortic wall. Animal Model:BALB/c mice Dosage:30 mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; for 24 hours Result:Reduced the lung bacterial load in murine model of pneumonic plague.Animal Model:C57BL/6J mice Dosage:100 mg/kg Administration:Oral gavage; daily, for 4 weeks Result:Had aortic destruction that was accompanied by decreased LOX expression and increased MMP expression and activity.Animal Model:C57BL/6J mice Dosage:100 mg/kg Administration:Oral gavage; daily, for 4 weeks Result:Caused mitochondrial DNA and nuclear DNA damage, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production. Increased apoptosis and necroptosis in the aortic wall.
-
SynonymsBay-09867 hydrochloride monohydrate | Ciloxan | Ceprimax | Oftacilox
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorBacterial
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
IndicationInfections of the genitourinary system respiratory tract gastrointestinal tract
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number86393-32-0
-
Formula Weight385.8
-
Molecular FormulaC17H21ClFN3O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:8 mg/mL (20.74 mM)H2O:10 mg/mL (25.92 mM)
-
SMILESCl.O.O=C(O)c1cn(C2CC2)c2cc(N3CCNCC3)c(F)cc2c1=O
-
Chemical Name1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrate hydrochloride
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hamblin K A Armstrong S J Barnes K B et al. Inhaled Liposomal Ciprofloxacin Protects against a Lethal Infection in a Murine Model of Pneumonic Plague[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017 8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Polygodial
Polygodial is an antifungal potentiator and an antibiotic, particularly against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida utilis, and Sclerotinia libertiana.
-
Norvancomycin hydroc...
An antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections that acts by inhibiting proper cell wall synthesis.
-
Pactamycin
Pactamycin (NSC 52947) is a potent protein synthesis inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


